The Ultimate Guide To Excel Formulas and Functions
Microsoft Excel has been frequently referred to as the world’s greatest calculator. Excel can create an unlimited number of different calculations. Once a few basic steps are mastered, a world of calculation options are available to any Excel user.
Building formulas and working with functions in Excel are core skills that need to be understood in order to really use Excel effectively. With that in mind, we decided to put together a complete set of tutorials from excerpts of our Excel Formulas and Functions class and offer it to you at no charge.
Once, you learn the basics about creating formulas in Excel, you will be able to use your spreadsheet data to perform calculations which will communicate valuable business trends and information to your team and to clients. When used effectively, formulas and functions will be one of your most powerful tools available to analyze your business data.
The guide is set up so you can learn how to create and modify formulas in step-by-step format. Students can go through the lessons in order, or hop to a topic that you want to focus on. There are practice files mentioned in most of the training videos that can be downloaded here.
This is a core skill in Excel, and once you learn it, you will be glad you did. So, let’s get started…
How to Create a Formula in Excel
When working with data in Excel, you will sometimes want to use formulas and functions to perform calculations on your data. Formulas are mathematical equations you can manually enter into cells to perform calcuations on your data. Functions are pre-written equations that Excel provides to help you perform simple and complex calculations more quickly.
Step 1: Select the cell where you would like the formula to appear, and enter the = sign.
Each formula needs to begin with the equal sign. The equal sign ( = ) instructs Excel that the information included after the equal sign should be calculated. You can enter the equal sign in the selected cell, or in the formula bar.
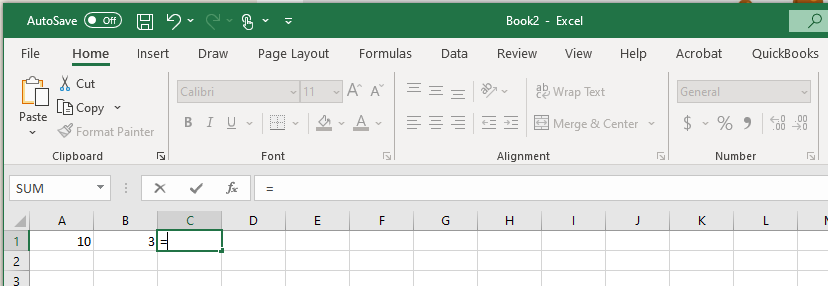
Step 2: Enter the formula arguments
After you enter the equal sign, you will enter the arguments for the calculation. This can be done in a few different ways: Using static variables, using cell references, or using Excel functions.
Static Variable Formulas
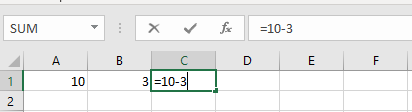
Cell Reference Formulas
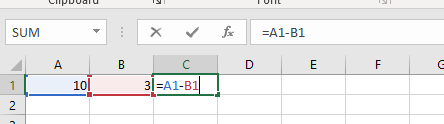
Formula Using Excel Functions
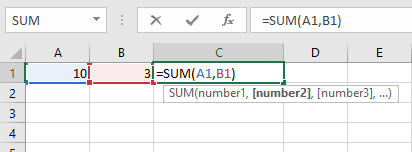
Step 3: Click the Enter Key, or Checkmark on Formula Bar
Once, you enter the formula arguements, click the enter key, and the result of the calculation will appear in the cell where you wrote the formula. That is it. Now you have a completed Excel formula. In the next section, we will look at how to apply a custom chart template to a new set of data.
How to Edit a Formula in Excel
Step 1: Double click on the Cell where the formula is located.
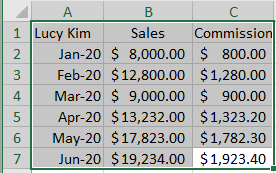
Use your mouse to select the data you would like to include in your chart.
Step 2: Make any changes needed to the formula
Once the chart data is selected, click in the Insert tab to display insert Chart options on the ribbon.
Step 3: Click on the Enter Key
In the Chart section of the Insert tab, move you mouse to the bottom right corner, then click the See All Charts button.
Step 4: Click on the All Charts tab in the Insert Chart window
In the Insert Chart window, click on the All Charts tab.
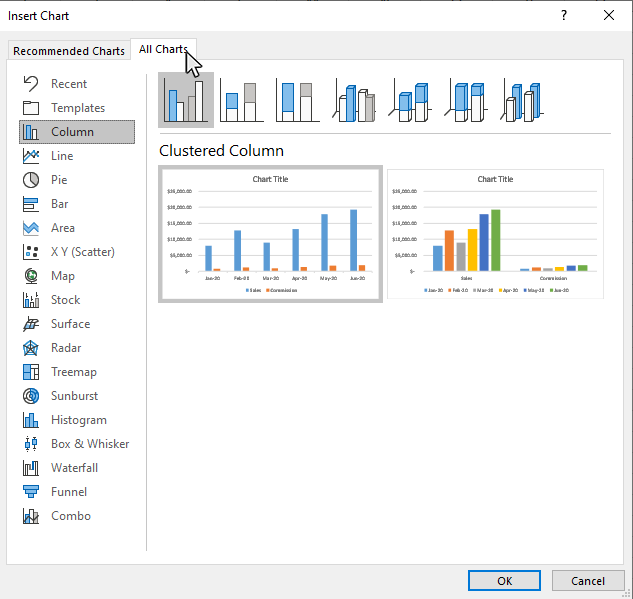
Step 5: Click on the Templates option on the All Charts tab
In the Chart section of the Insert tab, move you mouse to the bottom right corner, then click the See All Charts button.
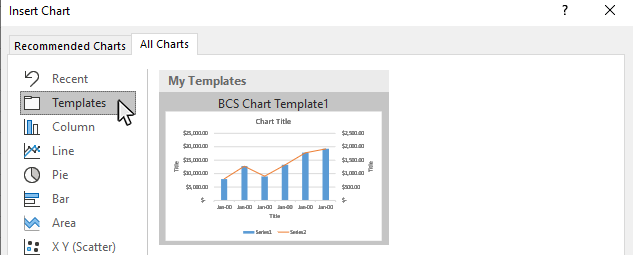
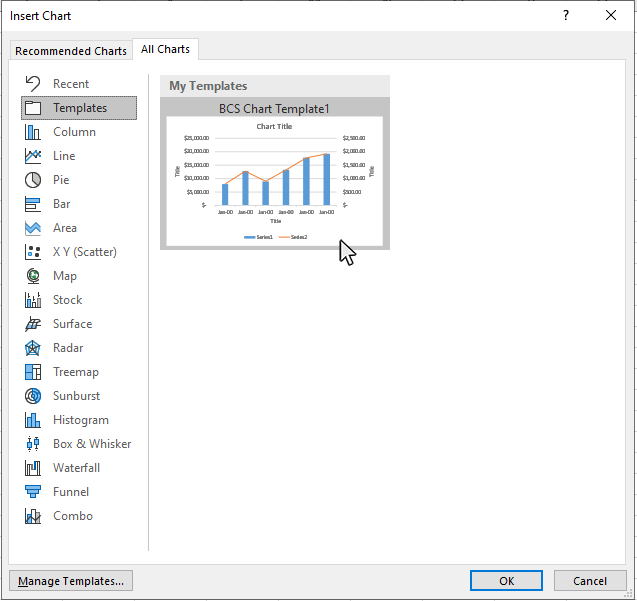
Step 6: Select the custom template you want to use, and click OK
Pick the template you want to use from the templates screen and click OK.
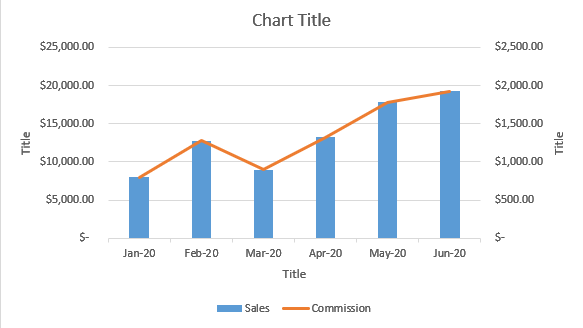
Excel will then apply the template formatting to the new chart.
How to use a Function in Excel
Absolute and Relative References in Excel
One of the most important concepts in Excel is cell addressing or cell references. Cell references are the way to tell Excel which cell we want to get data from when using formulas and functions.
There are three types of cell references used in Excel:
- Absolute References
- Relative References
- Mixed References
By default, Excel uses what is known as A1 notation when referring the location of cells. The column letter is followed by the row number to provide the definitive location of a cell. Notice in our example the active cell is in column A and row 5, the Name Box confirms A5 as the cell reference.
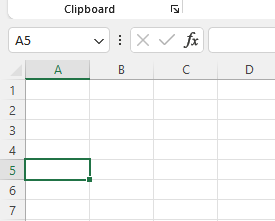
There are two types of cell reference: Absolute and Relative. The cell references behave differently when copied to other cells. The relative references change when a formula is copied to another cell. The absolute references, on the other hand, remain constant no matter where they are copied.
The default cell reference in Excel is relative. When a formula is copied to multiple location on the worksheet cell references change to match the new location. This is particularly helpful when the same formula is going to be needed in several cells.
In this example, a supervisor wants to keep track of the weekly pay of staff. The formula is quite simple – rate time hours worked (=f2*e2). All that is needed is to enter the formula once in g2. Then using the fill handle (small box in lower righthand corner of active cell) and perform a drag and drop to fill in all necessary cells.
Using Relative Cell References:


This use of relative addressing is a perfect example of how Excel can save so much time for users.

Relative cell addressing does not always provide the necessary results. Sometimes a constant is required to provide accurate answers. The $ is used to make parts of the cell address constant (locked down). There is a keyboard shortcut, f4, that can be used to make cell addresses constant.
An enhancement to the previous example will demonstrate the need of constant cell reference. Not only does the supervisor need to calculate weekly pay, but each employee receives the weekly bonus of $225.00. Simply adding A2 to the previous formula does not quite work if the same techniques is used.


Note: The weekly bonus is in cell A2 and is the same for all employees. In the range of cells from H2 to H9, A2 should be in each formula.
Using Absolute Cell References:
The previous example could be corrected by manually entering each formula individually or by changing A2 to an Absolute Cell Reference. The new formula in h2 will look like this: =g2+$a$2. As the drag and drop is completed from H2 through H9, notice how each weekly pay calculation has A2 added to it.


More Absolute Cell reference Options:
As mentioned earlier in this tutorial Excel uses A1 notation. When changing from Relative Reference to Absolute Reference there are additional conditions that need to be considered. Cells can be absolute, rows and be absolute and columns can be absolute. When using the keyboard shortcut F4, Excel circles through four settings. First – Cell in a constant, Second – Row is constant, Third – Row is absolute and Four – Cell is back to relative.
$A$2 Cell is absolute A$2 Row is absolute $A2 Column is absoluteOrder of Operations in Excel
How to Display Functions in Excel
Nested Functions in Excel
How to Copy a Formula in Excel
Types of Functions in Excel
Microsoft Excel currently has around 440 functions available for use in a variety of disciplines
The functions are grouped into these categories:
- Cube Functions
- Database Functions
- Date and Time Functions
- Engineering Functions
- Financial Functions
- Information Functions
- Logical Functions
- Lookup and Reference Functions
- Math and Trigonometry Functions
- Statistical Functions
- Web Functions
Popluar Excel Functions
Here is a list of widely used Excel Functions.
Cube Functions
CUBEKPIMEMBER function
Usage: The CUBEKPIMEMBER function is used to calculate a key performance indicator (KPI) property and displays the KPI name in the cell. A KPI is a quantifiable measurement, such as monthly gross profit or quarterly employee turnover, that is used to monitor an organization's performance..
Syntax:The syntax for the CUBEKPIMEMBERfunction is =CUBEKPIMEMBER(connection, kpi_name, kpi_property, [caption]).
CUBEMEMBER function
Usage: The CUBEMEMBER function is used to calculate a member or tuple from the cube. Use to validate that the member or tuple exists in the cube..
Syntax:The syntax for the CUBEMEMBERfunction is =CUBEMEMBER(connection, member_expression, [caption]).
CUBEMEMBERPROPERTY function
Usage: The CUBEMEMBERPROPERTY function is used to calculate the value of a member property from the cube. Use to validate that a member name exists within the cube and to return the specified property for this member..
Syntax:The syntax for the CUBEMEMBERPROPERTYfunction is =CUBEMEMBERPROPERTY(connection, member_expression, property).
CUBERANKEDMEMBER function
Usage: The CUBERANKEDMEMBER function is used to calculate the nth, or ranked, member in a set. Use to return one or more elements in a set, such as the top sales performer or the top 10 students..
Syntax:The syntax for the CUBERANKEDMEMBERfunction is =CUBERANKEDMEMBER(connection, set_expression, rank, [caption]).
CUBESET function
Usage: The CUBESET function is used to Defines a calculated set of members or tuples by sending a set expression to the cube on the server, which creates the set, and then returns that set to Microsoft Office Excel..
Syntax:The syntax for the CUBESETfunction is =CUBESET(connection, set_expression, [caption], [sort_order], [sort_by]).
CUBESETCOUNT function
Usage: The CUBESETCOUNT function is used to calculate the number of items in a set..
Syntax:The syntax for the CUBESETCOUNTfunction is =CUBESETCOUNT(set).
CUBEVALUE function
Usage: The CUBEVALUE function is used to calculate an aggregated value from the cube..
Syntax:The syntax for the CUBEVALUEfunction is =CUBEVALUE(connection, [member_expression1], [member_expression2], …).
Database Functions
DAVERAGE function
Usage: The DAVERAGE function is used to calculate the average of selected database entries.
Syntax:The syntax for the DAVERAGEfunction is =DAVERAGE(database, field, criteria).
DCOUNT function
Usage: The DCOUNT function is used to count the cells that contain numbers in a database.
Syntax:The syntax for the DCOUNTfunction is =DCOUNT(database, field, criteria).
DCOUNTA function
Usage: The DCOUNTA function is used to count nonblank cells in a database.
Syntax:The syntax for the DCOUNTAfunction is =DCOUNTA(database, field, criteria).
DGET function
Usage: The DGET function is used to extract a single record from a database that matches the specified criteria.
Syntax:The syntax for the DGETfunction is =DGET(database, field, criteria).
DMAX function
Usage: The DMAX function is used to calculate the maximum value from selected database entries.
Syntax:The syntax for the DMAXfunction is =DMAX(database, field, criteria).
DMIN function
Usage: The DMIN function is used to calculate the minimum value from selected database entries.
Syntax:The syntax for the DMINfunction is =DMIN(database, field, criteria).
DPRODUCT function
Usage: The DPRODUCT function is used to multiply the values in a particular field of records that match the criteria in a database.
Syntax:The syntax for the DPRODUCTfunction is =DPRODUCT(database, field, criteria).
DSTDEV function
Usage: The DSTDEV function is used to estimate the standard deviation based on a sample of selected database entries.
Syntax:The syntax for the DSTDEVfunction is =DSTDEV(database, field, criteria).
DSTDEVP function
Usage: The DSTDEVP function is used to Calculates the standard deviation based on the entire population of selected database entries.
Syntax:The syntax for the DSTDEVPfunction is =DSTDEVP(database, field, criteria).
DSUM function
Usage: The DSUM function is used to add the numbers in the field column of records in the database that match the criteria.
Syntax:The syntax for the DSUMfunction is =DSUM(database, field, criteria).
DVAR function
Usage: The DVAR function is used to estimates variance based on a sample from selected database entries.
Syntax:The syntax for the DVARfunction is =DVAR(database, field, criteria).
DVARP function
Usage: The DVARP function is used to Calculates variance based on the entire population of selected database entries.
Syntax:The syntax for the DVARPfunction is =DVAR(database, field, criteria).
Date and Time Functions
DATE function
Usage: The DATE function is used to calculate the serial number of a particular date.
Syntax:The syntax for the DATEfunction is =DATE(year,month,day).
DATEDIF function
Usage: The DATEDIF function is used to Calculates the number of days, months, or years between two dates. This function is useful in formulas where you need to calculate an age..
Syntax:The syntax for the DATEDIFfunction is =DATEDIF(start_date,end_date,unit).
DATEVALUE function
Usage: The DATEVALUE function is used to convert a date in the form of text to a serial number.
Syntax:The syntax for the DATEVALUEfunction is =DATEVALUE(date_text).
DAY function
Usage: The DAY function is used to convert a serial number to a day of the month.
Syntax:The syntax for the DAYfunction is =DAY(serial_number).
DAYS function
Usage: The DAYS function is used to calculate the number of days between two dates.
Syntax:The syntax for the DAYSfunction is =DAYS(end_date, start_date).
DAYS360 function
Usage: The DAYS360 function is used to Calculates the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year.
Syntax:The syntax for the DAYS360function is =DAYS360(start_date,end_date,[method]).
EDATE function
Usage: The EDATE function is used to calculate the serial number of the date that is the indicated number of months before or after the start date.
Syntax:The syntax for the EDATEfunction is =EDATE(start_date, months).
EOMONTH function
Usage: The EOMONTH function is used to calculate the serial number of the last day of the month before or after a specified number of months.
Syntax:The syntax for the EOMONTHfunction is =EOMONTH(start_date, months).
HOUR function
Usage: The HOUR function is used to convert a serial number to an hour.
Syntax:The syntax for the HOURfunction is =HOUR(serial_number).
ISOWEEKNUM function
Usage: The ISOWEEKNUM function is used to calculate the number of the ISO week number of the year for a given date.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISOWEEKNUMfunction is =ISOWEEKNUM(date).
MINUTE function
Usage: The MINUTE function is used to convert a serial number to a minute.
Syntax:The syntax for the MINUTEfunction is =MINUTE(serial_number).
MONTH function
Usage: The MONTH function is used to convert a serial number to a month.
Syntax:The syntax for the MONTHfunction is =MONTH(serial_number).
NETWORKDAYS function
Usage: The NETWORKDAYS function is used to calculate the number of whole workdays between two dates.
Syntax:The syntax for the NETWORKDAYSfunction is =NETWORKDAYS(start_date, end_date, [holidays]).
NETWORKDAYS.INTL function
Usage: The NETWORKDAYS.INTL function is used to calculate the number of whole workdays between two dates using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days.
Syntax:The syntax for the NETWORKDAYS.INTLfunction is =NETWORKDAYS.INTL(start_date, end_date, [weekend], [holidays]).
NOW function
Usage: The NOW function is used to calculate the serial number of the current date and time.
Syntax:The syntax for the NOWfunction is =NOW().
SECOND function
Usage: The SECOND function is used to convert a serial number to a second.
Syntax:The syntax for the SECONDfunction is =SECOND(serial_number).
TIME function
Usage: The TIME function is used to calculate the serial number of a particular time.
Syntax:The syntax for the TIMEfunction is =TIME(hour, minute, second).
TIMEVALUE function
Usage: The TIMEVALUE function is used to convert a time in the form of text to a serial number.
Syntax:The syntax for the TIMEVALUEfunction is =TIMEVALUE(time_text).
TODAY function
Usage: The TODAY function is used to calculate the serial number of today's date.
Syntax:The syntax for the TODAYfunction is =TODAY().
WEEKDAY function
Usage: The WEEKDAY function is used to convert a serial number to a day of the week.
Syntax:The syntax for the WEEKDAYfunction is =WEEKDAY(serial_number,[return_type]).
WEEKNUM function
Usage: The WEEKNUM function is used to convert a serial number to a number representing where the week falls numerically with a year.
Syntax:The syntax for the WEEKNUMfunction is =WEEKNUM(serial_number,[return_type]).
WORKDAY function
Usage: The WORKDAY function is used to calculate the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays.
Syntax:The syntax for the WORKDAYfunction is =WORKDAY(start_date, days, [holidays]).
WORKDAY.INTL function
Usage: The WORKDAY.INTL function is used to calculate the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days.
Syntax:The syntax for the WORKDAY.INTLfunction is =WORKDAY.INTL(start_date, days, [weekend], [holidays]).
YEAR function
Usage: The YEAR function is used to convert a serial number to a year.
Syntax:The syntax for the YEARfunction is =YEAR(serial_number).
YEARFRAC function
Usage: The YEARFRAC function is used to calculate the year fraction representing the number of whole days between start_date and end_date.
Syntax:The syntax for the YEARFRACfunction is =YEARFRAC(start_date, end_date, [basis]).
Engineering Functions
BESSELI function
Usage: The BESSELI function is used to calculate the modified Bessel function In(x).
Syntax:The syntax for the BESSELIfunction is =BESSELI(X, N).
BESSELJ function
Usage: The BESSELJ function is used to calculate the Bessel function Jn(x).
Syntax:The syntax for the BESSELJfunction is =BESSELJ(x,n).
BESSELK function
Usage: The BESSELK function is used to calculate the modified Bessel function Kn(x).
Syntax:The syntax for the BESSELKfunction is =BESSELK(x,n).
BESSELY function
Usage: The BESSELY function is used to calculate the Bessel function Yn(x).
Syntax:The syntax for the BESSELYfunction is =BESSELY(x,n).
BIN2DEC function
Usage: The BIN2DEC function is used to convert a binary number to decimal.
Syntax:The syntax for the BIN2DECfunction is =BIN2DEC(number).
BIN2HEX function
Usage: The BIN2HEX function is used to convert a binary number to hexadecimal.
Syntax:The syntax for the BIN2HEXfunction is =BIN2HEX(number, places).
BIN2OCT function
Usage: The BIN2OCT function is used to convert a binary number to octal.
Syntax:The syntax for the BIN2OCTfunction is =BIN2OCT(number, places).
BITAND function
Usage: The BITAND function is used to calculate a 'Bitwise And' of two numbers.
Syntax:The syntax for the BITANDfunction is =BITAND(number1, number2).
BITLSHIFT function
Usage: The BITLSHIFT function is used to calculate a value number shifted left by shift_amount bits.
Syntax:The syntax for the BITLSHIFTfunction is =BITLSHIFT(number, shift_amount).
BITOR function
Usage: The BITOR function is used to calculate a bitwise OR of 2 numbers.
Syntax:The syntax for the BITORfunction is =BITOR(number1, number2).
BITRSHIFT function
Usage: The BITRSHIFT function is used to calculate a value number shifted right by shift_amount bits.
Syntax:The syntax for the BITRSHIFTfunction is =BITRSHIFT(number, shift_amount).
BITXOR function
Usage: The BITXOR function is used to calculate a bitwise 'Exclusive Or' of two numbers.
Syntax:The syntax for the BITXORfunction is =BITXOR(number1, number2).
COMPLEX function
Usage: The COMPLEX function is used to convert real and imaginary coefficients into a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the COMPLEXfunction is =COMPLEX(real_num, i_num, [suffix]).
CONVERT function
Usage: The CONVERT function is used to convert a number from one measurement system to another.
Syntax:The syntax for the CONVERTfunction is =CONVERT(number,from_unit,to_unit).
DEC2BIN function
Usage: The DEC2BIN function is used to convert a decimal number to binary.
Syntax:The syntax for the DEC2BINfunction is =DEC2BIN(number, places).
DEC2HEX function
Usage: The DEC2HEX function is used to convert a decimal number to hexadecimal.
Syntax:The syntax for the DEC2HEXfunction is =DEC2HEX(number, places).
DEC2OCT function
Usage: The DEC2OCT function is used to convert a decimal number to octal.
Syntax:The syntax for the DEC2OCTfunction is =DEC2OCT(number, places).
DELTA function
Usage: The DELTA function is used to test whether two values are equal.
Syntax:The syntax for the DELTAfunction is =DELTA(number1, number2).
ERF function
Usage: The ERF function is used to calculate the error function.
Syntax:The syntax for the ERFfunction is =ERF(lower_limit,[upper_limit]).
ERF.PRECISE function
Usage: The ERF.PRECISE function is used to calculate the error function.
Syntax:The syntax for the ERF.PRECISEfunction is =ERF.PRECISE(x).
ERFC function
Usage: The ERFC function is used to calculate the complementary error function.
Syntax:The syntax for the ERFCfunction is =ERFC(x).
ERFC.PRECISE function
Usage: The ERFC.PRECISE function is used to calculate the complementary ERF function integrated between x and infinity.
Syntax:The syntax for the ERFC.PRECISEfunction is =ERFC.PRECISE(x).
GESTEP function
Usage: The GESTEP function is used to test whether a number is greater than a threshold value.
Syntax:The syntax for the GESTEPfunction is =GESTEP(number, [step]).
HEX2BIN function
Usage: The HEX2BIN function is used to convert a hexadecimal number to binary.
Syntax:The syntax for the HEX2BINfunction is =HEX2BIN(number, places).
HEX2DEC function
Usage: The HEX2DEC function is used to convert a hexadecimal number to decimal.
Syntax:The syntax for the HEX2DECfunction is =HEX2DEC(number).
HEX2OCT function
Usage: The HEX2OCT function is used to convert a hexadecimal number to octal.
Syntax:The syntax for the HEX2OCTfunction is =HEX2OCT(number, places).
IMABS function
Usage: The IMABS function is used to calculate the absolute value (modulus) of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMABSfunction is =IMABS(inumber).
IMAGINARY function
Usage: The IMAGINARY function is used to calculate the imaginary coefficient of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMAGINARYfunction is =IMAGINARY(inumber).
IMARGUMENT function
Usage: The IMARGUMENT function is used to calculate the argument theta, an angle expressed in radians.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMARGUMENTfunction is =IMARGUMENT(inumber).
IMCONJUGATE function
Usage: The IMCONJUGATE function is used to calculate the complex conjugate of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMCONJUGATEfunction is =IMCONJUGATE(inumber).
IMCOS function
Usage: The IMCOS function is used to calculate the cosine of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMCOSfunction is =IMCOS(inumber).
IMCOSH function
Usage: The IMCOSH function is used to calculate the hyperbolic cosine of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMCOSHfunction is =IMCOSH(inumber).
IMCOT function
Usage: The IMCOT function is used to calculate the cotangent of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMCOTfunction is =IMCOT(inumber).
IMCSC function
Usage: The IMCSC function is used to calculate the cosecant of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMCSCfunction is =IMCSC(inumber).
IMCSCH function
Usage: The IMCSCH function is used to calculate the hyperbolic cosecant of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMCSCHfunction is =IMCSCH(inumber).
IMDIV function
Usage: The IMDIV function is used to calculate the quotient of two complex numbers.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMDIVfunction is =IMDIV(inumber1, inumber2).
IMEXP function
Usage: The IMEXP function is used to calculate the exponential of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMEXPfunction is =IMEXP(inumber).
IMLN function
Usage: The IMLN function is used to calculate the natural logarithm of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMLNfunction is =IMLN(inumber).
IMLOG10 function
Usage: The IMLOG10 function is used to calculate the base-10 logarithm of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMLOG10function is =IMLOG10(inumber).
IMLOG2 function
Usage: The IMLOG2 function is used to calculate the base-2 logarithm of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMLOG2function is =IMLOG2(inumber).
IMPOWER function
Usage: The IMPOWER function is used to calculate a complex number raised to an integer power.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMPOWERfunction is =IMPOWER(inumber,number).
IMPRODUCT function
Usage: The IMPRODUCT function is used to calculate the product of from 2 to 255 complex numbers.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMPRODUCTfunction is =IMPRODUCT(inumber1, inumber2).
IMREAL function
Usage: The IMREAL function is used to calculate the real coefficient of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMREALfunction is =IMREAL(inumber).
IMSEC function
Usage: The IMSEC function is used to calculate the secant of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMSECfunction is =IMSEC(inumber).
IMSECH function
Usage: The IMSECH function is used to calculate the hyperbolic secant of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMSECHfunction is =IMSECH(inumber).
IMSIN function
Usage: The IMSIN function is used to calculate the sine of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMSINfunction is =IMSIN(inumber).
IMSINH function
Usage: The IMSINH function is used to calculate the hyperbolic sine of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMSINHfunction is =IMSINH(inumber).
IMSQRT function
Usage: The IMSQRT function is used to calculate the square root of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMSQRTfunction is =IMSQRT(inumber).
IMSUB function
Usage: The IMSUB function is used to calculate the difference between two complex numbers.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMSUBfunction is =IMSUB(inumber1, inumber2).
IMSUM function
Usage: The IMSUM function is used to calculate the sum of complex numbers.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMSUMfunction is =IMSUM(inumber1, inumber2).
IMTAN function
Usage: The IMTAN function is used to calculate the tangent of a complex number.
Syntax:The syntax for the IMTANfunction is =IMTAN(inumber).
OCT2BIN function
Usage: The OCT2BIN function is used to convert an octal number to binary.
Syntax:The syntax for the OCT2BINfunction is =OCT2BIN(number, places).
OCT2DEC function
Usage: The OCT2DEC function is used to convert an octal number to decimal.
Syntax:The syntax for the OCT2DECfunction is =OCT2DEC(number).
OCT2HEX function
Usage: The OCT2HEX function is used to convert an octal number to hexadecimal.
Syntax:The syntax for the OCT2HEXfunction is =OCT2HEX(number, places).
Financial Functions
ACCRINT function
Usage: The ACCRINT function is used to calculate the accrued interest for a security that pays periodic interest.
Syntax:The syntax for the ACCRINTfunction is =ACCRINT(issue, first_interest, settlement, rate, par, frequency, [basis], [calc_method]).
ACCRINTM function
Usage: The ACCRINTM function is used to calculate the accrued interest for a security that pays interest at maturity.
Syntax:The syntax for the ACCRINTMfunction is =ACCRINTM(issue, settlement, rate, par, [basis]).
AMORDEGRC function
Usage: The AMORDEGRC function is used to calculate the depreciation for each accounting period by using a depreciation coefficient.
Syntax:The syntax for the AMORDEGRCfunction is =AMORDEGRC(cost, date_purchased, first_period, salvage, period, rate, [basis]).
AMORLINC function
Usage: The AMORLINC function is used to calculate the depreciation for each accounting period.
Syntax:The syntax for the AMORLINCfunction is =AMORLINC(cost, date_purchased, first_period, salvage, period, rate, [basis]).
COUPDAYBS function
Usage: The COUPDAYBS function is used to calculate the number of days from the beginning of the coupon period to the settlement date.
Syntax:The syntax for the COUPDAYBSfunction is =COUPDAYBS(settlement, maturity, frequency, [basis]).
COUPDAYS function
Usage: The COUPDAYS function is used to calculate the number of days in the coupon period that contains the settlement date.
Syntax:The syntax for the COUPDAYSfunction is =COUPDAYS(settlement, maturity, frequency, [basis]).
COUPDAYSNC function
Usage: The COUPDAYSNC function is used to calculate the number of days from the settlement date to the next coupon date.
Syntax:The syntax for the COUPDAYSNCfunction is =COUPDAYSNC(settlement, maturity, frequency, [basis]).
COUPNCD function
Usage: The COUPNCD function is used to calculate the next coupon date after the settlement date.
Syntax:The syntax for the COUPNCDfunction is =COUPNCD(settlement, maturity, frequency, [basis]).
COUPNUM function
Usage: The COUPNUM function is used to calculate the number of coupons payable between the settlement date and maturity date.
Syntax:The syntax for the COUPNUMfunction is =COUPNUM(settlement, maturity, frequency, [basis]).
COUPPCD function
Usage: The COUPPCD function is used to calculate the previous coupon date before the settlement date.
Syntax:The syntax for the COUPPCDfunction is =COUPPCD(settlement, maturity, frequency, [basis]).
CUMIPMT function
Usage: The CUMIPMT function is used to calculate the cumulative interest paid between two periods.
Syntax:The syntax for the CUMIPMTfunction is =CUMIPMT(rate, nper, pv, start_period, end_period, type).
CUMPRINC function
Usage: The CUMPRINC function is used to calculate the cumulative principal paid on a loan between two periods.
Syntax:The syntax for the CUMPRINCfunction is =CUMPRINC(rate, nper, pv, start_period, end_period, type).
DB function
Usage: The DB function is used to calculate the depreciation of an asset for a specified period by using the fixed-declining balance method.
Syntax:The syntax for the DBfunction is =DB(cost, salvage, life, period, [month]).
DDB function
Usage: The DDB function is used to calculate the depreciation of an asset for a specified period by using the double-declining balance method or some other method that you specify.
Syntax:The syntax for the DDBfunction is =DDB(cost, salvage, life, period, [factor]).
DISC function
Usage: The DISC function is used to calculate the discount rate for a security.
Syntax:The syntax for the DISCfunction is =DISC(settlement, maturity, pr, redemption, [basis]).
DOLLARDE function
Usage: The DOLLARDE function is used to convert a dollar price, expressed as a fraction, into a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number.
Syntax:The syntax for the DOLLARDEfunction is =DOLLARDE(fractional_dollar, fraction).
DOLLARFR function
Usage: The DOLLARFR function is used to convert a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number, into a dollar price, expressed as a fraction.
Syntax:The syntax for the DOLLARFRfunction is =DOLLARFR(decimal_dollar, fraction).
DURATION function
Usage: The DURATION function is used to calculate the annual duration of a security with periodic interest payments.
Syntax:The syntax for the DURATIONfunction is =DURATION(settlement, maturity, coupon, yld, frequency, [basis]).
EFFECT function
Usage: The EFFECT function is used to calculate the effective annual interest rate.
Syntax:The syntax for the EFFECTfunction is =EFFECT(nominal_rate, npery).
FV function
Usage: The FV function is used to calculate the future value of an investment.
Syntax:The syntax for the FVfunction is =FV(rate,nper,pmt,[pv],[type]).
FVSCHEDULE function
Usage: The FVSCHEDULE function is used to calculate the future value of an initial principal after applying a series of compound interest rates.
Syntax:The syntax for the FVSCHEDULEfunction is =FVSCHEDULE(principal, schedule).
INTRATE function
Usage: The INTRATE function is used to calculate the interest rate for a fully invested security.
Syntax:The syntax for the INTRATEfunction is =INTRATE(settlement, maturity, investment, redemption, [basis]).
IPMT function
Usage: The IPMT function is used to calculate the interest payment for an investment for a given period.
Syntax:The syntax for the IPMTfunction is =IPMT(rate, per, nper, pv, [fv], [type]).
IRR function
Usage: The IRR function is used to calculate the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows.
Syntax:The syntax for the IRRfunction is =IRR(values, [guess]).
ISPMT function
Usage: The ISPMT function is used to Calculates the interest paid during a specific period of an investment.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISPMTfunction is =ISPMT(rate, per, nper, pv).
MDURATION function
Usage: The MDURATION function is used to calculate the Macauley modified duration for a security with an assumed par value of $100.
Syntax:The syntax for the MDURATIONfunction is =MDURATION(settlement, maturity, coupon, yld, frequency, [basis]).
MIRR function
Usage: The MIRR function is used to calculate the internal rate of return where positive and negative cash flows are financed at different rates.
Syntax:The syntax for the MIRRfunction is =MIRR(values, finance_rate, reinvest_rate).
NOMINAL function
Usage: The NOMINAL function is used to calculate the annual nominal interest rate.
Syntax:The syntax for the NOMINALfunction is =NOMINAL(effect_rate, npery).
NPER function
Usage: The NPER function is used to calculate the number of periods for an investment.
Syntax:The syntax for the NPERfunction is =NPER(rate,pmt,pv,[fv],[type]).
NPV function
Usage: The NPV function is used to calculate the net present value of an investment based on a series of periodic cash flows and a discount rate.
Syntax:The syntax for the NPVfunction is =NPV(rate,value1,[value2],...).
ODDFPRICE function
Usage: The ODDFPRICE function is used to calculate the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd first period.
Syntax:The syntax for the ODDFPRICEfunction is =ODDFPRICE(settlement, maturity, issue, first_coupon, rate, yld, redemption, frequency, [basis]).
ODDFYIELD function
Usage: The ODDFYIELD function is used to calculate the yield of a security with an odd first period.
Syntax:The syntax for the ODDFYIELDfunction is =ODDFYIELD(settlement, maturity, issue, first_coupon, rate, pr, redemption, frequency, [basis]).
ODDLPRICE function
Usage: The ODDLPRICE function is used to calculate the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd last period.
Syntax:The syntax for the ODDLPRICEfunction is =ODDLPRICE(settlement, maturity, last_interest, rate, yld, redemption, frequency, [basis]).
ODDLYIELD function
Usage: The ODDLYIELD function is used to calculate the yield of a security with an odd last period.
Syntax:The syntax for the ODDLYIELDfunction is =ODDLYIELD(settlement, maturity, last_interest, rate, pr, redemption, frequency, [basis]).
PDURATION function
Usage: The PDURATION function is used to calculate the number of periods required by an investment to reach a specified value.
Syntax:The syntax for the PDURATIONfunction is =PDURATION(rate, pv, fv).
PMT function
Usage: The PMT function is used to calculate the periodic payment for an annuity.
Syntax:The syntax for the PMTfunction is =PMT(rate, nper, pv, [fv], [type]).
PPMT function
Usage: The PPMT function is used to calculate the payment on the principal for an investment for a given period.
Syntax:The syntax for the PPMTfunction is =PPMT(rate, per, nper, pv, [fv], [type]).
PRICE function
Usage: The PRICE function is used to calculate the price per $100 face value of a security that pays periodic interest.
Syntax:The syntax for the PRICEfunction is =PRICE(settlement, maturity, rate, yld, redemption, frequency, [basis]).
PRICEDISC function
Usage: The PRICEDISC function is used to calculate the price per $100 face value of a discounted security.
Syntax:The syntax for the PRICEDISCfunction is =PRICEDISC(settlement, maturity, discount, redemption, [basis]).
PRICEMAT function
Usage: The PRICEMAT function is used to calculate the price per $100 face value of a security that pays interest at maturity.
Syntax:The syntax for the PRICEMATfunction is =PRICEMAT(settlement, maturity, issue, rate, yld, [basis]).
PV function
Usage: The PV function is used to calculate the present value of an investment.
Syntax:The syntax for the PVfunction is =PV(rate, nper, pmt, [fv], [type]).
RATE function
Usage: The RATE function is used to calculate the interest rate per period of an annuity.
Syntax:The syntax for the RATEfunction is =RATE(nper, pmt, pv, [fv], [type], [guess]).
RECEIVED function
Usage: The RECEIVED function is used to calculate the amount received at maturity for a fully invested security.
Syntax:The syntax for the RECEIVEDfunction is =RECEIVED(settlement, maturity, investment, discount, [basis]).
RRI function
Usage: The RRI function is used to calculate an equivalent interest rate for the growth of an investment.
Syntax:The syntax for the RRIfunction is =RRI(nper, pv, fv).
SLN function
Usage: The SLN function is used to calculate the straight-line depreciation of an asset for one period.
Syntax:The syntax for the SLNfunction is =SLN(cost, salvage, life).
SYD function
Usage: The SYD function is used to calculate the sum-of-years' digits depreciation of an asset for a specified period.
Syntax:The syntax for the SYDfunction is =SYD(cost, salvage, life, per).
TBILLEQ function
Usage: The TBILLEQ function is used to calculate the bond-equivalent yield for a Treasury bill.
Syntax:The syntax for the TBILLEQfunction is =TBILLEQ(settlement, maturity, discount).
TBILLPRICE function
Usage: The TBILLPRICE function is used to calculate the price per $100 face value for a Treasury bill.
Syntax:The syntax for the TBILLPRICEfunction is =TBILLPRICE(settlement, maturity, discount).
TBILLYIELD function
Usage: The TBILLYIELD function is used to calculate the yield for a Treasury bill.
Syntax:The syntax for the TBILLYIELDfunction is =TBILLYIELD(settlement, maturity, pr).
VDB function
Usage: The VDB function is used to calculate the depreciation of an asset for a specified or partial period by using a declining balance method.
Syntax:The syntax for the VDBfunction is =VDB(cost, salvage, life, start_period, end_period, [factor], [no_switch]).
XIRR function
Usage: The XIRR function is used to calculate the internal rate of return for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic.
Syntax:The syntax for the XIRRfunction is =XIRR(values, dates, [guess]).
XNPV function
Usage: The XNPV function is used to calculate the net present value for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic.
Syntax:The syntax for the XNPVfunction is =XNPV(rate, values, dates).
YIELD function
Usage: The YIELD function is used to calculate the yield on a security that pays periodic interest.
Syntax:The syntax for the YIELDfunction is =YIELD(settlement, maturity, rate, pr, redemption, frequency, [basis]).
YIELDDISC function
Usage: The YIELDDISC function is used to calculate the annual yield for a discounted security; for example, a Treasury bill.
Syntax:The syntax for the YIELDDISCfunction is =YIELDDISC(settlement, maturity, pr, redemption, [basis]).
YIELDMAT function
Usage: The YIELDMAT function is used to calculate the annual yield of a security that pays interest at maturity.
Syntax:The syntax for the YIELDMATfunction is =YIELDMAT(settlement, maturity, issue, rate, pr, [basis]).
Information Functions
CELL function
Usage: The CELL function is used to calculate information about the formatting, location, or contents of a cell.
Syntax:The syntax for the CELLfunction is =CELL(info_type,reference).
ERROR.TYPE function
Usage: The ERROR.TYPE function is used to calculate a number corresponding to an error type.
Syntax:The syntax for the ERROR.TYPEfunction is =ERROR.TYPE(error_val).
INFO function
Usage: The INFO function is used to calculate information about the current operating environment.
Syntax:The syntax for the INFOfunction is =INFO(type_text).
ISBLANK function
Usage: The ISBLANK function is used to calculate TRUE if the value is blank.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISBLANKfunction is =ISBLANK(value).
ISERR function
Usage: The ISERR function is used to calculate TRUE if the value is any error value except #N/A.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISERRfunction is =ISERR(value).
ISERROR function
Usage: The ISERROR function is used to calculate TRUE if the value is any error value.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISERRORfunction is =ISERROR(value).
ISEVEN function
Usage: The ISEVEN function is used to calculate TRUE if the number is even.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISEVENfunction is =ISEVEN(number).
ISFORMULA function
Usage: The ISFORMULA function is used to calculate TRUE if there is a reference to a cell that contains a formula.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISFORMULAfunction is =ISFORMULA(reference).
ISLOGICAL function
Usage: The ISLOGICAL function is used to calculate TRUE if the value is a logical value.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISLOGICALfunction is =ISLOGICAL(value).
ISNA function
Usage: The ISNA function is used to calculate TRUE if the value is the #N/A error value.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISNAfunction is =ISNA(value).
ISNONTEXT function
Usage: The ISNONTEXT function is used to calculate TRUE if the value is not text.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISNONTEXTfunction is =ISNONTEXT(value).
ISNUMBER function
Usage: The ISNUMBER function is used to calculate TRUE if the value is a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISNUMBERfunction is =ISNUMBER(value).
ISODD function
Usage: The ISODD function is used to calculate TRUE if the number is odd.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISODDfunction is =ISODD(number).
ISREF function
Usage: The ISREF function is used to calculate TRUE if the value is a reference.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISREFfunction is =ISREF(value).
ISTEXT function
Usage: The ISTEXT function is used to calculate TRUE if the value is text.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISTEXTfunction is =ISTEXT(value).
N function
Usage: The N function is used to calculate a value converted to a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the Nfunction is =N(value).
NA function
Usage: The NA function is used to calculate the error value #N/A.
Syntax:The syntax for the NAfunction is =NA().
SHEET function
Usage: The SHEET function is used to calculate the sheet number of the referenced sheet.
Syntax:The syntax for the SHEETfunction is =SHEET(value).
SHEETS function
Usage: The SHEETS function is used to calculate the number of sheets in a reference.
Syntax:The syntax for the SHEETSfunction is =SHEETS(reference).
TYPE function
Usage: The TYPE function is used to calculate a number indicating the data type of a value.
Syntax:The syntax for the TYPEfunction is =TYPE(value).
Logical Functions
AND function
Usage: The AND function is used to calculate TRUE if all of its arguments are TRUE.
Syntax:The syntax for the ANDfunction is =AND(logical1, [logical2], ...).
FALSE function
Usage: The FALSE function is used to calculate the logical value FALSE.
Syntax:The syntax for the FALSEfunction is =FALSE().
IF function
Usage: The IF function is used to specify a logical test to perform.
Syntax:The syntax for the IFfunction is =IF(logical_test, value_if_true, [value_if_false]).
IFERROR function
Usage: The IFERROR function is used to calculate a value you specify if a formula evaluates to an error; otherwise, returns the result of the formula.
Syntax:The syntax for the IFERRORfunction is =IFERROR(value, value_if_error).
IFNA function
Usage: The IFNA function is used to calculate the value you specify if the expression resolves to #N/A, otherwise returns the result of the expression.
Syntax:The syntax for the IFNAfunction is =IFNA(value, value_if_na).
IFS function
Usage: The IFS function is used to check whether one or more conditions are met and returns a value that corresponds to the first TRUE condition..
Syntax:The syntax for the IFSfunction is =IFS(logical_test1, value_if_true1, [logical_test2, value_if_true2], [logical_test3, value_if_true3],…).
NOT function
Usage: The NOT function is used to reverse the logic of its argument.
Syntax:The syntax for the NOTfunction is =NOT(logical).
OR function
Usage: The OR function is used to calculate TRUE if any argument is TRUE.
Syntax:The syntax for the ORfunction is =OR(logical1, [logical2], ...).
SWITCH function
Usage: The SWITCH function is used to evaluate an expression against a list of values and returns the result corresponding to the first matching value. If there is no match, an optional default value may be returned..
Syntax:The syntax for the SWITCHfunction is =SWITCH(expression, value1, result1, [default or value2, result2],…[default or value3, result3]).
TRUE function
Usage: The TRUE function is used to calculate the logical value TRUE.
Syntax:The syntax for the TRUEfunction is =TRUE().
XOR function
Usage: The XOR function is used to calculate a logical exclusive OR of all arguments.
Syntax:The syntax for the XORfunction is =XOR(logical1, [logical2],…).
Lookup and Reference Functions
ADDRESS function
Usage: The ADDRESS function is used to calculate a reference as text to a single cell in a worksheet.
Syntax:The syntax for the ADDRESSfunction is =ADDRESS(row_num, column_num, [abs_num], [a1], [sheet_text]).
AREAS function
Usage: The AREAS function is used to calculate the number of areas in a reference.
Syntax:The syntax for the AREASfunction is =AREAS(reference).
CHOOSE function
Usage: The CHOOSE function is used to choose a value from a list of values.
Syntax:The syntax for the CHOOSEfunction is =CHOOSE(index_num, value1, [value2], ...).
COLUMN function
Usage: The COLUMN function is used to calculate the column number of a reference.
Syntax:The syntax for the COLUMNfunction is =COLUMN(reference).
COLUMNS function
Usage: The COLUMNS function is used to calculate the number of columns in a reference.
Syntax:The syntax for the COLUMNSfunction is =COLUMNS(array).
FILTER function
Usage: The FILTER function is used to filter a range of data based on criteria you define.
Syntax:The syntax for the FILTERfunction is =FILTER(array,include,[if_empty]).
FORMULATEXT function
Usage: The FORMULATEXT function is used to calculate the formula at the given reference as text.
Syntax:The syntax for the FORMULATEXTfunction is =FORMULATEXT(reference).
GETPIVOTDATA function
Usage: The GETPIVOTDATA function is used to calculate data stored in a PivotTable report.
Syntax:The syntax for the GETPIVOTDATAfunction is =GETPIVOTDATA(data_field, pivot_table, [field1, item1, field2, item2], ...).
HLOOKUP function
Usage: The HLOOKUP function is used to look in the top row of an array and returns the value of the indicated cell.
Syntax:The syntax for the HLOOKUPfunction is =HLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, row_index_num, [range_lookup]).
HYPERLINK function
Usage: The HYPERLINK function is used to create a shortcut or jump that opens a document stored on a network server, an intranet, or the Internet.
Syntax:The syntax for the HYPERLINKfunction is =HYPERLINK(link_location, [friendly_name]).
INDEX function
Usage: The INDEX function is used to use an index to choose a value from a reference or array.
Syntax:The syntax for the INDEXfunction is =INDEX().
INDIRECT function
Usage: The INDIRECT function is used to calculate a reference indicated by a text value.
Syntax:The syntax for the INDIRECTfunction is =INDIRECT(ref_text, [a1]).
LOOKUP function
Usage: The LOOKUP function is used to look up values in a vector or array.
Syntax:The syntax for the LOOKUPfunction is =LOOKUP().
MATCH function
Usage: The MATCH function is used to look up values in a reference or array.
Syntax:The syntax for the MATCHfunction is =MATCH(lookup_value, lookup_array, [match_type]).
OFFSET function
Usage: The OFFSET function is used to calculate a reference offset from a given reference.
Syntax:The syntax for the OFFSETfunction is =OFFSET(reference, rows, cols, [height], [width]).
ROW function
Usage: The ROW function is used to calculate the row number of a reference.
Syntax:The syntax for the ROWfunction is =ROW(reference).
ROWS function
Usage: The ROWS function is used to calculate the number of rows in a reference.
Syntax:The syntax for the ROWSfunction is =ROWS(array).
RTD function
Usage: The RTD function is used to retrieve real-time data from a program that supports COM automation.
Syntax:The syntax for the RTDfunction is =RTD(ProgID, server, topic1, [topic2], ...).
SORT function
Usage: The SORT function is used to sort the contents of a range or array.
Syntax:The syntax for the SORTfunction is =SORT(array,[sort_index],[sort_order],[by_col]).
SORTBY function
Usage: The SORTBY function is used to sort the contents of a range or array based on the values in a corresponding range or array.
Syntax:The syntax for the SORTBYfunction is =SORTBY(array, by_array1, [sort_order1], [by_array2, sort_order2],…) .
TRANSPOSE function
Usage: The TRANSPOSE function is used to calculate the transpose of an array.
Syntax:The syntax for the TRANSPOSEfunction is =TRANSPOSE(array).
UNIQUE function
Usage: The UNIQUE function is used to calculate a list of unique values in a list or range.
Syntax:The syntax for the UNIQUEfunction is =UNIQUE(array,[by_col],[exactly_once]).
VLOOKUP function
Usage: The VLOOKUP function is used to look in the first column of an array and moves across the row to return the value of a cell.
Syntax:The syntax for the VLOOKUPfunction is =VLOOKUP (lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup]).
XLOOKUP function
Usage: The XLOOKUP function is used to search a range or an array, and returns an item corresponding to the first match it finds. If a match doesn't exist, then XLOOKUP can return the closest (approximate) match. .
Syntax:The syntax for the XLOOKUPfunction is =XLOOKUP(lookup_value, lookup_array, return_array, [if_not_found], [match_mode], [search_mode]).
XMATCH function
Usage: The XMATCH function is used to calculate the relative position of an item in an array or range of cells. .
Syntax:The syntax for the XMATCHfunction is =XMATCH(lookup_value, lookup_array, [match_mode], [search_mode]) .
Math and Trigonometry Functions
ABS function
Usage: The ABS function is used to calculate the absolute value of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the ABSfunction is =ABS(number).
ACOS function
Usage: The ACOS function is used to calculate the arccosine of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the ACOSfunction is =ACOS(number).
ACOSH function
Usage: The ACOSH function is used to calculate the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the ACOSHfunction is =ACOSH(number).
ACOT function
Usage: The ACOT function is used to calculate the arccotangent of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the ACOTfunction is =ACOT(number).
ACOTH function
Usage: The ACOTH function is used to calculate the hyperbolic arccotangent of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the ACOTHfunction is =ACOTH(number).
AGGREGATE function
Usage: The AGGREGATE function is used to calculate an aggregate in a list or database.
Syntax:The syntax for the AGGREGATEfunction is =AGGREGATE(function_num, options, ref1, [ref2], …).
ARABIC function
Usage: The ARABIC function is used to convert a Roman number to Arabic, as a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the ARABICfunction is =ARABIC(text).
ASIN function
Usage: The ASIN function is used to calculate the arcsine of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the ASINfunction is =ASIN(number).
ASINH function
Usage: The ASINH function is used to calculate the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the ASINHfunction is =ASINH(number).
ATAN function
Usage: The ATAN function is used to calculate the arctangent of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the ATANfunction is =ATAN(number).
ATAN2 function
Usage: The ATAN2 function is used to calculate the arctangent from x- and y-coordinates.
Syntax:The syntax for the ATAN2function is =ATAN2(x_num, y_num).
ATANH function
Usage: The ATANH function is used to calculate the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the ATANHfunction is =ATANH(number).
BASE function
Usage: The BASE function is used to convert a number into a text representation with the given radix (base).
Syntax:The syntax for the BASEfunction is =BASE(Number, Radix [Min_length]).
CEILING function
Usage: The CEILING function is used to rounds a number to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance.
Syntax:The syntax for the CEILINGfunction is =CEILING(number, significance).
CEILING.MATH function
Usage: The CEILING.MATH function is used to rounds a number up, to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance.
Syntax:The syntax for the CEILING.MATHfunction is =CEILING.MATH(number, [significance], [mode]).
CEILING.PRECISE function
Usage: The CEILING.PRECISE function is used to rounds a number the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance. Regardless of the sign of the number, the number is rounded up..
Syntax:The syntax for the CEILING.PRECISEfunction is =CEILING.PRECISE(number).
COMBIN function
Usage: The COMBIN function is used to calculate the number of combinations for a given number of objects.
Syntax:The syntax for the COMBINfunction is =COMBIN(number, number_chosen).
COMBINA function
Usage: The COMBINA function is used to calculate the number of combinations with repetitions for a given number of items.
Syntax:The syntax for the COMBINAfunction is =COMBINA(number, number_chosen).
COS function
Usage: The COS function is used to calculate the cosine of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the COSfunction is =COS(number).
COSH function
Usage: The COSH function is used to calculate the hyperbolic cosine of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the COSHfunction is =COSH(number).
COT function
Usage: The COT function is used to calculate the cotangent of an angle.
Syntax:The syntax for the COTfunction is =COT(number).
COTH function
Usage: The COTH function is used to calculate the hyperbolic cotangent of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the COTHfunction is =COTH(number).
CSC function
Usage: The CSC function is used to calculate the cosecant of an angle.
Syntax:The syntax for the CSCfunction is =CSC(number).
CSCH function
Usage: The CSCH function is used to calculate the hyperbolic cosecant of an angle.
Syntax:The syntax for the CSCHfunction is =CSCH(number).
DECIMAL function
Usage: The DECIMAL function is used to converts a text representation of a number in a given base into a decimal number.
Syntax:The syntax for the DECIMALfunction is =DECIMAL(number,radix).
DEGREES function
Usage: The DEGREES function is used to converts radians to degrees.
Syntax:The syntax for the DEGREESfunction is =DEGREES(angle).
EVEN function
Usage: The EVEN function is used to round a number up to the nearest even integer.
Syntax:The syntax for the EVENfunction is =EVEN(number).
EXP function
Usage: The EXP function is used to calculate e raised to the power of a given number.
Syntax:The syntax for the EXPfunction is =EXP(number).
FACT function
Usage: The FACT function is used to calculate the factorial of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the FACTfunction is =FACT(number).
FACTDOUBLE function
Usage: The FACTDOUBLE function is used to calculate the double factorial of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the FACTDOUBLEfunction is =FACTDOUBLE(number).
FLOOR function
Usage: The FLOOR function is used to round a number down, toward zero.
Syntax:The syntax for the FLOORfunction is =FLOOR(number, significance).
FLOOR.MATH function
Usage: The FLOOR.MATH function is used to round a number down, to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance.
Syntax:The syntax for the FLOOR.MATHfunction is =FLOOR.MATH(number, significance, mode).
FLOOR.PRECISE function
Usage: The FLOOR.PRECISE function is used to round a number down to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance. Regardless of the sign of the number, the number is rounded down..
Syntax:The syntax for the FLOOR.PRECISEfunction is =FLOOR.PRECISE(number, [significance]).
GCD function
Usage: The GCD function is used to calculate the greatest common divisor.
Syntax:The syntax for the GCDfunction is =GCD(number1, [number2], ...).
INT function
Usage: The INT function is used to round a number down to the nearest integer.
Syntax:The syntax for the INTfunction is =INT(number).
ISO.CEILING function
Usage: The ISO.CEILING function is used to calculate a number that is rounded up to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance.
Syntax:The syntax for the ISO.CEILINGfunction is =ISO.CEILING(number, [significance]).
LCM function
Usage: The LCM function is used to calculate the least common multiple.
Syntax:The syntax for the LCMfunction is =LCM(number1, [number2], ...).
LET function
Usage: The LET function is used to assign names to calculation results to allow storing intermediate calculations, values, or defining names inside a formula.
Syntax:The syntax for the LETfunction is =LET(name, name_value, calculation).
LN function
Usage: The LN function is used to calculate the natural logarithm of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the LNfunction is =LN(number).
LOG function
Usage: The LOG function is used to calculate the logarithm of a number to a specified base.
Syntax:The syntax for the LOGfunction is =LOG(number, base).
LOG10 function
Usage: The LOG10 function is used to calculate the base-10 logarithm of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the LOG10function is =LOG10(number).
MDETERM function
Usage: The MDETERM function is used to calculate the matrix determinant of an array.
Syntax:The syntax for the MDETERMfunction is =MDETERM(array).
MINVERSE function
Usage: The MINVERSE function is used to calculate the matrix inverse of an array.
Syntax:The syntax for the MINVERSEfunction is =MINVERSE(array).
MMULT function
Usage: The MMULT function is used to calculate the matrix product of two arrays.
Syntax:The syntax for the MMULTfunction is =MMULT(array1, array2).
MOD function
Usage: The MOD function is used to calculate the remainder from division.
Syntax:The syntax for the MODfunction is =MOD(number, divisor).
MROUND function
Usage: The MROUND function is used to calculate a number rounded to the desired multiple.
Syntax:The syntax for the MROUNDfunction is =MROUND(number, multiple).
MULTINOMIAL function
Usage: The MULTINOMIAL function is used to calculate the multinomial of a set of numbers.
Syntax:The syntax for the MULTINOMIALfunction is =MULTINOMIAL(number1, [number2], ...).
MUNIT function
Usage: The MUNIT function is used to calculate the unit matrix or the specified dimension.
Syntax:The syntax for the MUNITfunction is =MUNIT(dimension).
ODD function
Usage: The ODD function is used to round a number up to the nearest odd integer.
Syntax:The syntax for the ODDfunction is =ODD(number).
PI function
Usage: The PI function is used to calculate the value of pi.
Syntax:The syntax for the PIfunction is =PI().
POWER function
Usage: The POWER function is used to calculate the result of a number raised to a power.
Syntax:The syntax for the POWERfunction is =POWER(number, power).
PRODUCT function
Usage: The PRODUCT function is used to multiply its arguments.
Syntax:The syntax for the PRODUCTfunction is =PRODUCT(number1, [number2], ...).
QUOTIENT function
Usage: The QUOTIENT function is used to calculate the integer portion of a division.
Syntax:The syntax for the QUOTIENTfunction is =QUOTIENT(numerator, denominator).
RADIANS function
Usage: The RADIANS function is used to convert degrees to radians.
Syntax:The syntax for the RADIANSfunction is =RADIANS(angle).
RAND function
Usage: The RAND function is used to calculate a random number between 0 and 1.
Syntax:The syntax for the RANDfunction is =RAND().
RANDARRAY function
Usage: The RANDARRAY function is used to calculate an array of random numbers between 0 and 1. However, you can specify the number of rows and columns to fill, minimum and maximum values, and whether to return whole numbers or decimal values..
Syntax:The syntax for the RANDARRAYfunction is =RANDARRAY([rows],[columns],[min],[max],[whole_number]).
RANDBETWEEN function
Usage: The RANDBETWEEN function is used to calculate a random number between the numbers you specify.
Syntax:The syntax for the RANDBETWEENfunction is =RANDBETWEEN(bottom, top).
ROMAN function
Usage: The ROMAN function is used to convert an Arabic numeral to Roman, as text.
Syntax:The syntax for the ROMANfunction is =ROMAN(number, [form]).
ROUND function
Usage: The ROUND function is used to round a number to a specified number of digits.
Syntax:The syntax for the ROUNDfunction is =ROUND(number, num_digits).
ROUNDDOWN function
Usage: The ROUNDDOWN function is used to round a number down, toward zero.
Syntax:The syntax for the ROUNDDOWNfunction is =ROUNDDOWN(number, num_digits).
ROUNDUP function
Usage: The ROUNDUP function is used to round a number up, away from zero.
Syntax:The syntax for the ROUNDUPfunction is =ROUNDUP(number, num_digits).
SEC function
Usage: The SEC function is used to calculate the secant of an angle.
Syntax:The syntax for the SECfunction is =SEC(number).
SECH function
Usage: The SECH function is used to calculate the hyperbolic secant of an angle.
Syntax:The syntax for the SECHfunction is =SECH(number).
SERIESSUM function
Usage: The SERIESSUM function is used to calculate the sum of a power series based on the formula.
Syntax:The syntax for the SERIESSUMfunction is =SERIESSUM(x, n, m, coefficients).
SEQUENCE function
Usage: The SEQUENCE function is used to generate a list of sequential numbers in an array, such as 1, 2, 3, 4.
Syntax:The syntax for the SEQUENCEfunction is =SEQUENCE(rows,[columns],[start],[step]).
SIGN function
Usage: The SIGN function is used to calculate the sign of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the SIGNfunction is =SIGN(number).
SIN function
Usage: The SIN function is used to calculate the sine of the given angle.
Syntax:The syntax for the SINfunction is =SIN(number).
SINH function
Usage: The SINH function is used to calculate the hyperbolic sine of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the SINHfunction is =SINH(number).
SQRT function
Usage: The SQRT function is used to calculate a positive square root.
Syntax:The syntax for the SQRTfunction is =SQRT(number).
SQRTPI function
Usage: The SQRTPI function is used to calculate the square root of (number * pi).
Syntax:The syntax for the SQRTPIfunction is =SQRTPI(number).
SUBTOTAL function
Usage: The SUBTOTAL function is used to calculate a subtotal in a list or database.
Syntax:The syntax for the SUBTOTALfunction is =SUBTOTAL(function_num,ref1,[ref2],...).
SUM function
Usage: The SUM function is used to add its arguments.
Syntax:The syntax for the SUMfunction is =SUM(number1,[number2],...).
SUMIF function
Usage: The SUMIF function is used to add the cells specified by a given criteria.
Syntax:The syntax for the SUMIFfunction is =SUMIF(range, criteria, [sum_range]).
SUMIFS function
Usage: The SUMIFS function is used to add the cells in a range that meet multiple criteria.
Syntax:The syntax for the SUMIFSfunction is =SUMIFS(sum_range, criteria_range1, criteria1, [criteria_range2, criteria2], ...).
SUMPRODUCT function
Usage: The SUMPRODUCT function is used to calculate the sum of the products of corresponding array components.
Syntax:The syntax for the SUMPRODUCTfunction is =SUMPRODUCT(array1, [array2], [array3], ...).
SUMSQ function
Usage: The SUMSQ function is used to calculate the sum of the squares of the arguments.
Syntax:The syntax for the SUMSQfunction is =SUMSQ(number1, [number2], ...).
SUMX2MY2 function
Usage: The SUMX2MY2 function is used to calculate the sum of the difference of squares of corresponding values in two arrays.
Syntax:The syntax for the SUMX2MY2function is =SUMX2MY2(array_x, array_y).
SUMX2PY2 function
Usage: The SUMX2PY2 function is used to calculate the sum of the sum of squares of corresponding values in two arrays.
Syntax:The syntax for the SUMX2PY2function is =SUMX2PY2(array_x, array_y).
SUMXMY2 function
Usage: The SUMXMY2 function is used to calculate the sum of squares of differences of corresponding values in two arrays.
Syntax:The syntax for the SUMXMY2function is =SUMXMY2(array_x, array_y).
TAN function
Usage: The TAN function is used to calculate the tangent of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the TANfunction is =TAN(number).
TANH function
Usage: The TANH function is used to calculate the hyperbolic tangent of a number.
Syntax:The syntax for the TANHfunction is =TANH(number).
TRUNC function
Usage: The TRUNC function is used to truncate a number to an integer.
Syntax:The syntax for the TRUNCfunction is =TRUNC(number, [num_digits]).
Statistical Functions
AVEDEV function
Usage: The AVEDEV function is used to calculate the average of the absolute deviations of data points from their mean.
Syntax:The syntax for the AVEDEVfunction is =AVEDEV(number1, [number2], ...).
AVERAGE function
Usage: The AVERAGE function is used to calculate the average of its arguments.
Syntax:The syntax for the AVERAGEfunction is =AVERAGE(number1, [number2], ...).
AVERAGEA function
Usage: The AVERAGEA function is used to calculate the average of its arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values.
Syntax:The syntax for the AVERAGEAfunction is =AVERAGEA(value1, [value2], ...).
AVERAGEIF function
Usage: The AVERAGEIF function is used to calculate the average (arithmetic mean) of all the cells in a range that meet a given criteria.
Syntax:The syntax for the AVERAGEIFfunction is =AVERAGEIF(range, criteria, [average_range]).
AVERAGEIFS function
Usage: The AVERAGEIFS function is used to calculate the average (arithmetic mean) of all cells that meet multiple criteria.
Syntax:The syntax for the AVERAGEIFSfunction is =AVERAGEIFS(average_range, criteria_range1, criteria1, [criteria_range2, criteria2], ...).
BETA.DIST function
Usage: The BETA.DIST function is used to calculate the beta cumulative distribution function.
Syntax:The syntax for the BETA.DISTfunction is =BETA.DIST(x,alpha,beta,cumulative,[A],[B]).
BETA.INV function
Usage: The BETA.INV function is used to calculate the inverse of the cumulative distribution function for a specified beta distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the BETA.INVfunction is =BETAINV(probability,alpha,beta,[A],[B]).
BINOM.DIST function
Usage: The BINOM.DIST function is used to calculate the individual term binomial distribution probability.
Syntax:The syntax for the BINOM.DISTfunction is =BINOM.DIST(number_s,trials,probability_s,cumulative).
BINOM.DIST.RANGE function
Usage: The BINOM.DIST.RANGE function is used to calculate the probability of a trial result using a binomial distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the BINOM.DIST.RANGEfunction is =BINOM.DIST.RANGE(trials,probability_s,number_s,[number_s2]).
BINOM.INV function
Usage: The BINOM.INV function is used to calculate the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is less than or equal to a criterion value.
Syntax:The syntax for the BINOM.INVfunction is =BINOM.INV(trials,probability_s,alpha).
CHISQ.DIST function
Usage: The CHISQ.DIST function is used to calculate the cumulative beta probability density function.
Syntax:The syntax for the CHISQ.DISTfunction is =CHISQ.DIST(x,deg_freedom,cumulative).
CHISQ.DIST.RT function
Usage: The CHISQ.DIST.RT function is used to calculate the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the CHISQ.DIST.RTfunction is =CHISQ.DIST.RT(x,deg_freedom).
CHISQ.INV function
Usage: The CHISQ.INV function is used to calculate the cumulative beta probability density function.
Syntax:The syntax for the CHISQ.INVfunction is =CHISQ.INV(probability,deg_freedom).
CHISQ.INV.RT function
Usage: The CHISQ.INV.RT function is used to calculate the inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the CHISQ.INV.RTfunction is =CHISQ.INV.RT(probability,deg_freedom).
CHISQ.TEST function
Usage: The CHISQ.TEST function is used to calculate the test for independence.
Syntax:The syntax for the CHISQ.TESTfunction is =CHISQ.TEST(actual_range,expected_range).
CONFIDENCE.NORM function
Usage: The CONFIDENCE.NORM function is used to calculate the confidence interval for a population mean.
Syntax:The syntax for the CONFIDENCE.NORMfunction is =CONFIDENCE.NORM(alpha,standard_dev,size).
CONFIDENCE.T function
Usage: The CONFIDENCE.T function is used to calculate the confidence interval for a population mean, using a Student's t distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the CONFIDENCE.Tfunction is =CONFIDENCE.T(alpha,standard_dev,size).
CORREL function
Usage: The CORREL function is used to calculate the correlation coefficient between two data sets.
Syntax:The syntax for the CORRELfunction is =CORREL(array1, array2).
COUNT function
Usage: The COUNT function is used to count how many numbers are in the list of arguments.
Syntax:The syntax for the COUNTfunction is =COUNT(value1, [value2], ...).
COUNTA function
Usage: The COUNTA function is used to count how many values are in the list of arguments.
Syntax:The syntax for the COUNTAfunction is =COUNTA(value1, [value2], ...).
COUNTBLANK function
Usage: The COUNTBLANK function is used to count the number of blank cells within a range.
Syntax:The syntax for the COUNTBLANKfunction is =COUNTBLANK(range).
COUNTIF function
Usage: The COUNTIF function is used to count the number of cells within a range that meet the given criteria.
Syntax:The syntax for the COUNTIFfunction is =COUNTIF(range, criteria).
COUNTIFS function
Usage: The COUNTIFS function is used to count the number of cells within a range that meet multiple criteria.
Syntax:The syntax for the COUNTIFSfunction is =COUNTIFS(criteria_range1, criteria1, [criteria_range2, criteria2]…).
COVARIANCE.P function
Usage: The COVARIANCE.P function is used to calculate covariance, the average of the products of paired deviations.
Syntax:The syntax for the COVARIANCE.Pfunction is =COVARIANCE.P(array1,array2).
COVARIANCE.S function
Usage: The COVARIANCE.S function is used to calculate the sample covariance, the average of the products deviations for each data point pair in two data sets.
Syntax:The syntax for the COVARIANCE.Sfunction is =COVARIANCE.S(array1,array2).
DEVSQ function
Usage: The DEVSQ function is used to calculate the sum of squares of deviations.
Syntax:The syntax for the DEVSQfunction is =DEVSQ(number1, [number2], ...).
EXPON.DIST function
Usage: The EXPON.DIST function is used to calculate the exponential distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the EXPON.DISTfunction is =EXPON.DIST(x,lambda,cumulative).
F.DIST function
Usage: The F.DIST function is used to calculate the F probability distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the F.DISTfunction is =F.DIST(x,deg_freedom1,deg_freedom2,cumulative).
F.DIST.RT function
Usage: The F.DIST.RT function is used to calculate the F probability distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the F.DIST.RTfunction is =F.DIST.RT(x,deg_freedom1,deg_freedom2).
F.INV function
Usage: The F.INV function is used to calculate the inverse of the F probability distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the F.INVfunction is =F.INV(probability,deg_freedom1,deg_freedom2).
F.INV.RT function
Usage: The F.INV.RT function is used to calculate the inverse of the F probability distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the F.INV.RTfunction is =F.INV.RT(probability,deg_freedom1,deg_freedom2).
F.TEST function
Usage: The F.TEST function is used to calculate the result of an F-test.
Syntax:The syntax for the F.TESTfunction is =F.TEST(array1,array2).
FISHER function
Usage: The FISHER function is used to calculate the Fisher transformation.
Syntax:The syntax for the FISHERfunction is =FISHER(x).
FISHERINV function
Usage: The FISHERINV function is used to calculate the inverse of the Fisher transformation.
Syntax:The syntax for the FISHERINVfunction is =FISHERINV(y).
FORECAST function
Usage: The FORECAST function is used to calculate a value along a linear trend.
Syntax:The syntax for the FORECASTfunction is =FORECAST(x, known_y's, known_x's).
FORECAST.ETS function
Usage: The FORECAST.ETS function is used to calculate a future value based on existing (historical) values by using the AAA version of the Exponential Smoothing (ETS) algorithm.
Syntax:The syntax for the FORECAST.ETSfunction is =FORECAST.ETS(target_date, values, timeline, [seasonality], [data_completion], [aggregation]).
FORECAST.ETS.CONFINT function
Usage: The FORECAST.ETS.CONFINT function is used to calculate a confidence interval for the forecast value at the specified target date.
Syntax:The syntax for the FORECAST.ETS.CONFINTfunction is =FORECAST.ETS.CONFINT(target_date, values, timeline, [confidence_level], [seasonality], [data_completion], [aggregation]).
FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function
Usage: The FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function is used to calculate the length of the repetitive pattern Excel detects for the specified time series.
Syntax:The syntax for the FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITYfunction is =FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY(values, timeline, [data_completion], [aggregation]).
FORECAST.ETS.STAT function
Usage: The FORECAST.ETS.STAT function is used to calculate a statistical value as a result of time series forecasting.
Syntax:The syntax for the FORECAST.ETS.STATfunction is =FORECAST.ETS.STAT(values, timeline, statistic_type, [seasonality], [data_completion], [aggregation]).
FORECAST.LINEAR function
Usage: The FORECAST.LINEAR function is used to calculate a future value based on existing values.
Syntax:The syntax for the FORECAST.LINEARfunction is =FORECAST.LINEAR(x, known_y's, known_x's).
FREQUENCY function
Usage: The FREQUENCY function is used to calculate a frequency distribution as a vertical array.
Syntax:The syntax for the FREQUENCYfunction is =FREQUENCY(data_array, bins_array).
GAMMA function
Usage: The GAMMA function is used to calculate the Gamma function value.
Syntax:The syntax for the GAMMAfunction is =GAMMA(number).
GAMMA.DIST function
Usage: The GAMMA.DIST function is used to calculate the gamma distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the GAMMA.DISTfunction is =GAMMA.DIST(x,alpha,beta,cumulative).
GAMMA.INV function
Usage: The GAMMA.INV function is used to calculate the inverse of the gamma cumulative distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the GAMMA.INVfunction is =GAMMA.INV(probability,alpha,beta).
GAMMALN function
Usage: The GAMMALN function is used to calculate the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x).
Syntax:The syntax for the GAMMALNfunction is =GAMMALN(x).
GAMMALN.PRECISE function
Usage: The GAMMALN.PRECISE function is used to calculate the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x).
Syntax:The syntax for the GAMMALN.PRECISEfunction is =GAMMALN.PRECISE(x).
GAUSS function
Usage: The GAUSS function is used to calculate 0.5 less than the standard normal cumulative distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the GAUSSfunction is =GAUSS(z).
GEOMEAN function
Usage: The GEOMEAN function is used to calculate the geometric mean.
Syntax:The syntax for the GEOMEANfunction is =GEOMEAN(number1, [number2], ...).
GROWTH function
Usage: The GROWTH function is used to calculate values along an exponential trend.
Syntax:The syntax for the GROWTHfunction is =GROWTH(known_y's, [known_x's], [new_x's], [const]).
HARMEAN function
Usage: The HARMEAN function is used to calculate the harmonic mean.
Syntax:The syntax for the HARMEANfunction is =HARMEAN(number1, [number2], ...).
HYPGEOM.DIST function
Usage: The HYPGEOM.DIST function is used to calculate the hypergeometric distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the HYPGEOM.DISTfunction is =HYPGEOM.DIST(sample_s,number_sample,population_s,number_pop,cumulative).
INTERCEPT function
Usage: The INTERCEPT function is used to calculate the intercept of the linear regression line.
Syntax:The syntax for the INTERCEPTfunction is =INTERCEPT(known_y's, known_x's).
KURT function
Usage: The KURT function is used to calculate the kurtosis of a data set.
Syntax:The syntax for the KURTfunction is =KURT(number1, [number2], ...).
LARGE function
Usage: The LARGE function is used to calculate the k-th largest value in a data set.
Syntax:The syntax for the LARGEfunction is =LARGE(array, k).
LINEST function
Usage: The LINEST function is used to calculate the parameters of a linear trend.
Syntax:The syntax for the LINESTfunction is =LINEST(known_y's, [known_x's], [const], [stats]).
LOGEST function
Usage: The LOGEST function is used to calculate the parameters of an exponential trend.
Syntax:The syntax for the LOGESTfunction is =LOGEST(known_y's, [known_x's], [const], [stats]).
LOGNORM.DIST function
Usage: The LOGNORM.DIST function is used to calculate the cumulative lognormal distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the LOGNORM.DISTfunction is =LOGNORM.DIST(x,mean,standard_dev,cumulative).
LOGNORM.INV function
Usage: The LOGNORM.INV function is used to calculate the inverse of the lognormal cumulative distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the LOGNORM.INVfunction is =LOGNORM.INV(probability, mean, standard_dev).
MAX function
Usage: The MAX function is used to calculate the maximum value in a list of arguments.
Syntax:The syntax for the MAXfunction is =MAX(number1, [number2], ...).
MAXA function
Usage: The MAXA function is used to calculate the maximum value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values.
Syntax:The syntax for the MAXAfunction is =MAXA(value1,[value2],...).
MAXIFS function
Usage: The MAXIFS function is used to calculate the maximum value among cells specified by a given set of conditions or criteria.
Syntax:The syntax for the MAXIFSfunction is =MAXIFS(max_range, criteria_range1, criteria1, [criteria_range2, criteria2], ...).
MEDIAN function
Usage: The MEDIAN function is used to calculate the median of the given numbers.
Syntax:The syntax for the MEDIANfunction is =MEDIAN(number1, [number2], ...).
MIN function
Usage: The MIN function is used to calculate the minimum value in a list of arguments.
Syntax:The syntax for the MINfunction is =MIN(number1, [number2], ...).
MINA function
Usage: The MINA function is used to calculate the smallest value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values.
Syntax:The syntax for the MINAfunction is =MINA(value1, [value2], ...).
MINIFS function
Usage: The MINIFS function is used to calculate the minimum value among cells specified by a given set of conditions or criteria..
Syntax:The syntax for the MINIFSfunction is =MINIFS(min_range, criteria_range1, criteria1, [criteria_range2, criteria2], ...).
MODE.MULT function
Usage: The MODE.MULT function is used to calculate a vertical array of the most frequently occurring, or repetitive values in an array or range of data.
Syntax:The syntax for the MODE.MULTfunction is =MODE.MULT((number1,[number2],...).
MODE.SNGL function
Usage: The MODE.SNGL function is used to calculate the most common value in a data set.
Syntax:The syntax for the MODE.SNGLfunction is =MODE.SNGL(number1,[number2],...).
NEGBINOM.DIST function
Usage: The NEGBINOM.DIST function is used to calculate the negative binomial distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the NEGBINOM.DISTfunction is =NEGBINOM.DIST(number_f,number_s,probability_s,cumulative).
NORM.DIST function
Usage: The NORM.DIST function is used to calculate the normal cumulative distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the NORM.DISTfunction is =NORM.DIST(x,mean,standard_dev,cumulative).
NORM.INV function
Usage: The NORM.INV function is used to calculate the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the NORM.INVfunction is =NORMINV(probability,mean,standard_dev).
NORM.S.DIST function
Usage: The NORM.S.DIST function is used to calculate the standard normal cumulative distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the NORM.S.DISTfunction is =NORM.S.DIST(z,cumulative).
NORM.S.INV function
Usage: The NORM.S.INV function is used to calculate the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the NORM.S.INVfunction is =NORM.S.INV(probability).
PEARSON function
Usage: The PEARSON function is used to calculate the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient.
Syntax:The syntax for the PEARSONfunction is =PEARSON(array1, array2).
PERCENTILE.EXC function
Usage: The PERCENTILE.EXC function is used to calculate the k-th percentile of values in a range, where k is in the range 0..1, exclusive.
Syntax:The syntax for the PERCENTILE.EXCfunction is =PERCENTILE.EXC(array,k).
PERCENTILE.INC function
Usage: The PERCENTILE.INC function is used to calculate the k-th percentile of values in a range.
Syntax:The syntax for the PERCENTILE.INCfunction is =PERCENTILE.INC(array,k).
PERCENTRANK.EXC function
Usage: The PERCENTRANK.EXC function is used to calculate the rank of a value in a data set as a percentage (0..1, exclusive) of the data set.
Syntax:The syntax for the PERCENTRANK.EXCfunction is =PERCENTRANK.EXC(array,x,[significance]).
PERCENTRANK.INC function
Usage: The PERCENTRANK.INC function is used to calculate the percentage rank of a value in a data set.
Syntax:The syntax for the PERCENTRANK.INCfunction is =PERCENTRANK.INC(array,x,[significance]).
PERMUT function
Usage: The PERMUT function is used to calculate the number of permutations for a given number of objects.
Syntax:The syntax for the PERMUTfunction is =PERMUT(number, number_chosen).
PERMUTATIONA function
Usage: The PERMUTATIONA function is used to calculate the number of permutations for a given number of objects (with repetitions) that can be selected from the total objects.
Syntax:The syntax for the PERMUTATIONAfunction is =PERMUTATIONA(number, number-chosen).
PHI function
Usage: The PHI function is used to calculate the value of the density function for a standard normal distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the PHIfunction is =PHI(x).
POISSON.DIST function
Usage: The POISSON.DIST function is used to calculate the Poisson distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the POISSON.DISTfunction is =POISSON.DIST(x,mean,cumulative).
PROB function
Usage: The PROB function is used to calculate the probability that values in a range are between two limits.
Syntax:The syntax for the PROBfunction is =PROB(x_range, prob_range, [lower_limit], [upper_limit]).
QUARTILE.EXC function
Usage: The QUARTILE.EXC function is used to calculate the quartile of the data set, based on percentile values from 0..1, exclusive.
Syntax:The syntax for the QUARTILE.EXCfunction is =QUARTILE.EXC(array, quart).
QUARTILE.INC function
Usage: The QUARTILE.INC function is used to calculate the quartile of a data set.
Syntax:The syntax for the QUARTILE.INCfunction is =QUARTILE.INC(array,quart).
RANK.AVG function
Usage: The RANK.AVG function is used to calculate the rank of a number in a list of numbers.
Syntax:The syntax for the RANK.AVGfunction is =RANK.AVG(number,ref,[order]).
RANK.EQ function
Usage: The RANK.EQ function is used to calculate the rank of a number in a list of numbers.
Syntax:The syntax for the RANK.EQfunction is =RANK.EQ(number,ref,[order]).
RSQ function
Usage: The RSQ function is used to calculate the square of the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient.
Syntax:The syntax for the RSQfunction is =RSQ(known_y's,known_x's).
SKEW function
Usage: The SKEW function is used to calculate the skewness of a distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the SKEWfunction is =SKEW(number1, [number2], ...).
SKEW.P function
Usage: The SKEW.P function is used to calculate the skewness of a distribution based on a population: a characterization of the degree of asymmetry of a distribution around its mean.
Syntax:The syntax for the SKEW.Pfunction is =SKEW.P(number 1, [number 2],…).
SLOPE function
Usage: The SLOPE function is used to calculate the slope of the linear regression line.
Syntax:The syntax for the SLOPEfunction is =SLOPE(known_y's, known_x's).
SMALL function
Usage: The SMALL function is used to calculate the k-th smallest value in a data set.
Syntax:The syntax for the SMALLfunction is =SMALL(array, k).
STANDARDIZE function
Usage: The STANDARDIZE function is used to calculate a normalized value.
Syntax:The syntax for the STANDARDIZEfunction is =STANDARDIZE(x, mean, standard_dev).
STDEV.P function
Usage: The STDEV.P function is used to Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population.
Syntax:The syntax for the STDEV.Pfunction is =STDEV.P(number1,[number2],...).
STDEV.S function
Usage: The STDEV.S function is used to estimate standard deviation based on a sample.
Syntax:The syntax for the STDEV.Sfunction is =STDEV.S(number1,[number2],...).
STDEVA function
Usage: The STDEVA function is used to estimate standard deviation based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values.
Syntax:The syntax for the STDEVAfunction is =STDEVA(value1, [value2], ...).
STDEVPA function
Usage: The STDEVPA function is used to Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values.
Syntax:The syntax for the STDEVPAfunction is =STDEVPA(value1, [value2], ...).
STEYX function
Usage: The STEYX function is used to calculate the standard error of the predicted y-value for each x in the regression.
Syntax:The syntax for the STEYXfunction is =STEYX(known_y's, known_x's).
T.DIST function
Usage: The T.DIST function is used to calculate the Percentage Points (probability) for the Student t-distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the T.DISTfunction is =T.DIST(x,deg_freedom, cumulative).
T.DIST.2T function
Usage: The T.DIST.2T function is used to calculate the Percentage Points (probability) for the Student t-distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the T.DIST.2Tfunction is =T.DIST.2T(x,deg_freedom).
T.DIST.RT function
Usage: The T.DIST.RT function is used to calculate the Student's t-distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the T.DIST.RTfunction is =T.DIST.RT(x,deg_freedom).
T.INV function
Usage: The T.INV function is used to calculate the t-value of the Student's t-distribution as a function of the probability and the degrees of freedom.
Syntax:The syntax for the T.INVfunction is =T.INV(probability,deg_freedom).
T.INV.2T function
Usage: The T.INV.2T function is used to calculate the inverse of the Student's t-distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the T.INV.2Tfunction is =T.INV.2T(probability,deg_freedom).
T.TEST function
Usage: The T.TEST function is used to calculate the probability associated with a Student's t-test.
Syntax:The syntax for the T.TESTfunction is =T.TEST(array1,array2,tails,type).
TREND function
Usage: The TREND function is used to calculate values along a linear trend.
Syntax:The syntax for the TRENDfunction is =TREND(known_y's, [known_x's], [new_x's], [const]).
TRIMMEAN function
Usage: The TRIMMEAN function is used to calculate the mean of the interior of a data set.
Syntax:The syntax for the TRIMMEANfunction is =TRIMMEAN(array, percent).
VAR.P function
Usage: The VAR.P function is used to Calculates variance based on the entire population.
Syntax:The syntax for the VAR.Pfunction is =VAR.P(number1,[number2],...).
VAR.S function
Usage: The VAR.S function is used to estimate variance based on a sample.
Syntax:The syntax for the VAR.Sfunction is =VAR.S(number1,[number2],...).
VARA function
Usage: The VARA function is used to estimate variance based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values.
Syntax:The syntax for the VARAfunction is =VARA(value1, [value2], ...).
VARPA function
Usage: The VARPA function is used to Calculates variance based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values.
Syntax:The syntax for the VARPAfunction is =VARPA(value1, [value2], ...).
WEIBULL.DIST function
Usage: The WEIBULL.DIST function is used to calculate the Weibull distribution.
Syntax:The syntax for the WEIBULL.DISTfunction is =WEIBULL.DIST(x,alpha,beta,cumulative).
Z.TEST function
Usage: The Z.TEST function is used to calculate the one-tailed probability-value of a z-test.
Syntax:The syntax for the Z.TESTfunction is =Z.TEST(array,x,[sigma]).
耀㽦䀀㺮Web Functions
ENCODEURL function
Usage: The ENCODEURL function is used to calculate a URL-encoded string.
Syntax:The syntax for the ENCODEURLfunction is =ENCODEURL(text).
FILTERXML function
Usage: The FILTERXML function is used to calculate specific data from the XML content by using the specified XPath.
Syntax:The syntax for the FILTERXMLfunction is =FILTERXML(xml, xpath).
WEBSERVICE function
Usage: The WEBSERVICE function is used to calculate data from a web service.
Syntax:The syntax for the WEBSERVICEfunction is =WEBSERVICE(url).
Topic #1
How to Create Formulas in Excel



